Research Articles
A Complete Guide to Paired-End RNA-seq Alignment with STAR: From Basics to Advanced Optimization
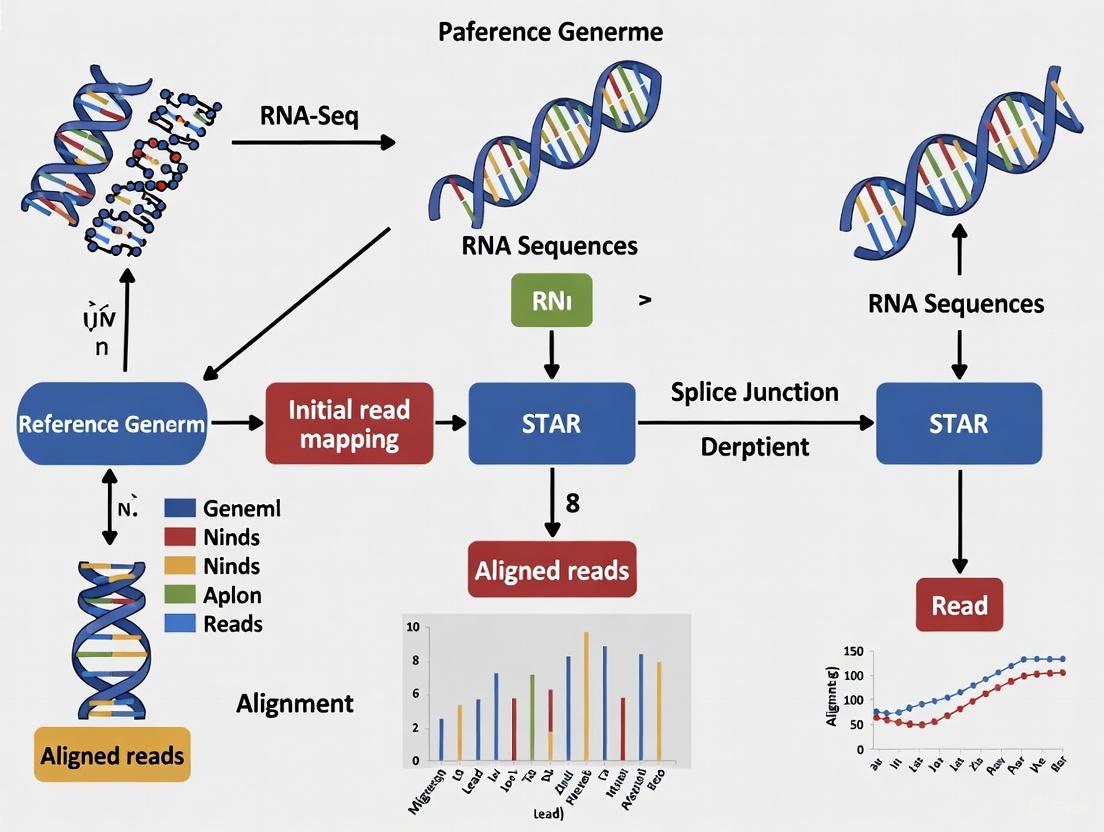
This article provides a comprehensive, step-by-step protocol for aligning paired-end RNA-seq reads using the Spliced Transcripts Alignment to a Reference (STAR) software. Tailored for researchers and scientists in drug development and biomedical research, it covers foundational concepts, detailed methodology, critical troubleshooting, and validation techniques. Readers will learn to perform both standard and advanced 2-pass mapping, optimize parameters for specific experimental goals like somatic mutation or fusion transcript detection, and interpret alignment outputs to ensure data quality for downstream differential expression and splicing analysis.
Optimizing STAR Alignment Parameters for Enhanced Novel Splice Junction Detection in Biomedical Research
This article provides a comprehensive guide for researchers and drug development professionals on optimizing the STAR aligner for novel splice junction detection, a critical capability for identifying disease-relevant splicing variants. We cover foundational concepts of spliced alignment, detail step-by-step protocols for two-pass alignment and parameter configuration, address common troubleshooting and optimization challenges, and present rigorous validation frameworks. By integrating current methodological insights with practical optimization strategies, this resource empowers scientists to maximize sensitivity and accuracy in splicing analyses, thereby advancing transcriptomic studies in cancer, neurodegeneration, and other splicing-associated diseases.
Optimizing STAR Genome Indexing for Human RNA-seq: A Complete Guide to Parameters, Troubleshooting, and Best Practices
This article provides a comprehensive guide for researchers and bioinformaticians on generating and optimizing a STAR genome index for the human genome, a critical first step in RNA-seq analysis. It covers foundational concepts of the STAR aligner's algorithm, a step-by-step methodological workflow for index generation with key parameters, solutions to common memory and performance issues, and guidance on validation and comparative analysis. The content is tailored to empower professionals in biomedical and clinical research to achieve accurate, efficient, and reproducible transcriptomic mapping, directly supporting downstream applications in gene expression quantification and biomarker discovery.
Pathway Enrichment Analysis: A Comprehensive Guide from Basics to Advanced Applications in Biomedicine
This article provides a complete guide to pathway enrichment analysis (PEA), a foundational bioinformatics method for interpreting gene lists from omics experiments. Tailored for researchers, scientists, and drug development professionals, it covers core concepts, statistical methods, and practical workflows. Readers will learn to define gene lists, select appropriate enrichment tools like g:Profiler and GSEA, and interpret results using visualization platforms such as Cytoscape and EnrichmentMap. The guide also addresses common pitfalls, optimization strategies for robust results, and advanced applications in drug repositioning and biomarker discovery, empowering users to confidently apply PEA in their research.
Accelerating Discovery: A 2025 Guide to High-Performance Genomic Analysis
As large-scale genomic sequencing becomes foundational to biomedical research and drug development, optimizing computational performance is no longer optional—it is critical. This article provides a comprehensive guide for researchers and scientists tackling the computational challenges of massive genomic datasets. We explore the core technologies reshaping the field, from AI-powered bioinformatics and cloud-native platforms to innovative methods like sparsified genomics. The guide offers practical methodologies for implementation, strategies for troubleshooting common bottlenecks, and a rigorous framework for pipeline validation and performance benchmarking, empowering teams to accelerate their research while ensuring robust, reproducible results.
De Novo Genome Assembly from Illumina Reads: A Comprehensive Guide from Foundation to Application
This article provides a comprehensive guide for researchers and drug development professionals on de novo genome assembly using Illumina short-read sequencing. It covers foundational principles, from defining de novo assembly and its advantages to critical pre-assembly planning, including assessing genome properties and DNA quality requirements. The guide details a complete methodological workflow, including quality control, assembly algorithms like de Bruijn graphs, and post-assembly polishing. It further addresses common challenges and optimization strategies for complex genomes and offers robust frameworks for assembly validation, quality assessment, and comparative genomics to ensure the generation of accurate, reliable reference sequences for downstream biomedical research.
The Invisible Architecture of Life: How Scientists Are Predicting Protein Structures
Explore the revolution in protein structure prediction, from AlphaFold breakthroughs to quaternary structure modeling and quality assessment methods.
Decoding the Genetic Blueprint of Colorectal Cancer: How Gene Mutations Drive Tumor Development
Explore the role of gene mutations in colorectal cancer development and the cutting-edge detection technologies revolutionizing personalized treatment approaches.
Unraveling Nature's Blueprint: How the BRCA1 Gene Reveals Sheep Evolutionary Secrets
Explore how whole sequence analysis of the BRCA1 gene reveals genetic diversity and evolutionary patterns in domestic and wild sheep populations.
Bioinformatics: A Calculated Discovery – Revisiting a Pivotal Moment in Computational Biology
Exploring the impact of the 2006 MCBIOS conference on computational biology and its lasting legacy in modern bioinformatics research.